Copper is a reddish-orange metal that is plentiful in nature. Copper ore can be found in many different ore minerals, among them chalcopyrite mineral, chalcocite mineral, covellite mineral, bornite mineral, azurite mineral, dioptase mineral, tennantite mineral, chrysocolla mineral, and digenite mineral. About half of the copper ore used currently comes from chalcopyrite ore. Read More…
Our company may have started small, but we quickly grew to handle the largest aluminum orders. Our metals are made from the highest quality materials, and we pledge to offer superior service to all our customers. We don’t want customers who use us one time, we want to establish lifelong relationships with customers that last generations. Contact us for more info!
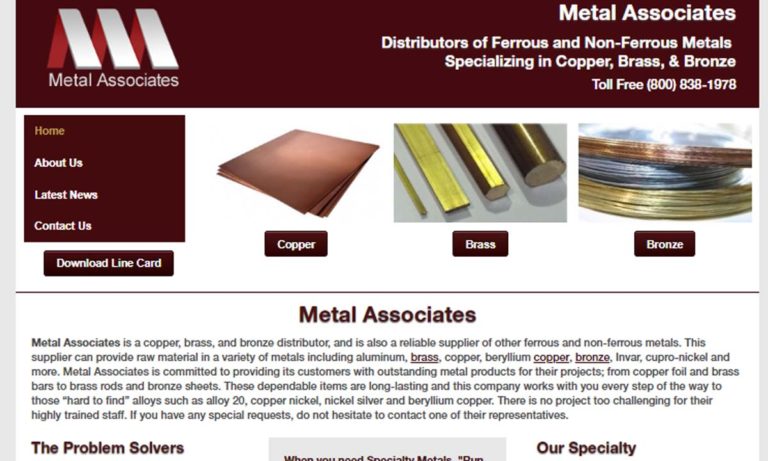
With over 25 years of metallurgy experience we guarantee we can produce exactly what you are looking for. We offer fast delivery and a multitude of beryllium copper sizes. Our highly knowledge staff takes great pride in creating these outstanding copper alloys. We have a reputation of manufacturing the best copper fabrications. Our company has risen in the standard in copper processing. Contact...
At Source 21, Inc., we take pride in offering top-notch copper products to meet a wide range of industrial and commercial needs. When it comes to copper, we've established ourselves as a reliable provider known for quality, accessibility, and customer satisfaction. Our extensive array of copper products is designed to cater to your diverse requirements while ensuring uncompromised excellence.

At ABC Metals, we are dedicated to delivering high-quality copper products that meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. We work with a wide range of copper materials, from pure copper to specialized alloys, to provide solutions that excel in conductivity, durability, and corrosion resistance.

At Southern Copper & Supply Company, we have built our reputation on delivering high-quality copper products and dependable supply solutions to meet the diverse needs of our customers. We specialize in sourcing, processing, and distributing copper in various forms, from raw stock and sheet material to precision-cut and custom-fabricated components.
More Copper Suppliers
Copper, identified by the chemical symbol Cu, is an essential industrial metal located in Group 11 of the periodic table with an atomic number of 29. Known for its unique characteristics, pure copper is soft, malleable, ductile, and nonmagnetic, making it an exceptional material for a wide range of applications. Additionally, copper is an outstanding electrical conductor and exhibits high thermal conductivity, which contributes to its widespread use in numerous industries including electronics, construction, renewable energy, and manufacturing.
A standout feature of copper is its ability to form alloys, greatly increasing its adaptability. Prominent alloys include bronze, which combines copper with tin (CuSn), and brass, made from copper and zinc (Cu3Zn2). By alloying with other metals, copper gains enhanced mechanical and chemical properties, expanding its utility across a wide array of industrial, commercial, and technological applications, where it plays a vital role in modern infrastructure and product design.
Applications of Copper: A Versatile Metal Across Industries
Copper, with the chemical symbol Cu and atomic number 29, is a Group 11 element in the periodic table renowned for its exceptional properties. Its softness, malleability, ductility, nonmagnetic nature, and superior conductivity of electricity and heat make it one of the most versatile metals in industrial manufacturing. Additionally, copper’s ability to form alloys like bronze (copper and tin, CuSn) and brass (copper and zinc, Cu3Zn2) enhances its utility, allowing it to adopt the properties of other metals. These characteristics make copper indispensable across a wide range of industries, from electrical engineering to construction, manufacturing, energy, telecommunications, and beyond. Below, we explore the key applications of copper and its alloys in various sectors and consider how they address specific buyer needs and project requirements.
-
- Electrical and Electronics Industry
Copper’s excellent electrical conductivity—second only to silver—makes it the material of choice for a vast range of electrical applications. If you’re asking, “Why is copper used for electrical wiring?” the answer lies in its combination of high conductivity, ductility, and corrosion resistance.
-
- Wiring and Cabling: Copper is widely used in electrical wiring for residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. Its high conductivity ensures efficient power transmission with minimal energy loss, making it the preferred material for power distribution networks and electrical grids.
- Motors and Transformers: Copper windings are essential in electric motors, transformers, and generators, where they enhance energy efficiency and performance due to low resistance. This is especially critical for high-performance industrial and transportation equipment.
- Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): Copper is used in PCBs for electronic devices like smartphones, computers, medical devices, and televisions, providing reliable electrical connections and supporting miniaturization in electronics manufacturing.
- Connectors and Terminals: Copper’s conductivity and corrosion resistance make it ideal for electrical connectors, terminals, and busbars in power systems, control panels, and renewable energy installations.
- Benefits: Copper’s high conductivity, durability, and resistance to corrosion ensure reliable and long-lasting electrical systems, reducing energy waste, maintenance costs, and system downtime.
Search prompt: What are the best types of copper wire for industrial electrical systems? How do you select copper alloys for high-voltage applications?
-
- Construction and Architecture
Copper’s durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal make it a popular material in construction and architectural applications. If you’re exploring, “What is copper used for in building construction?” the answer covers a wide array of structural and decorative roles.
-
- Roofing and Cladding: Copper is used for roofing, flashing, and cladding due to its longevity and ability to develop a protective patina—a greenish layer known as copper carbonate that forms over time, enhancing corrosion resistance. Iconic structures like the Statue of Liberty showcase this natural patina.
- Plumbing Systems: Copper pipes and fittings are widely used in plumbing for water supply lines, heating systems, and refrigeration. Copper’s resistance to corrosion and ability to withstand high temperatures make it ideal for these applications, ensuring clean water distribution and efficient thermal management.
- Electrical Installations: Copper wiring and grounding systems are standard in buildings to ensure safe and efficient electrical distribution, meeting building codes and safety standards.
- Decorative Elements: Copper’s reddish-brown color and ability to be shaped into intricate designs make it a favorite for architectural accents, sculptures, and interior decor.
- Benefits: Copper’s longevity (lasting decades without significant degradation), aesthetic versatility, low maintenance needs, and resistance to environmental factors make it a preferred material in both commercial and residential construction.
Search prompt: How do copper roofing materials compare to aluminum and zinc in terms of lifespan and maintenance?
-
- Industrial Manufacturing
Copper and its alloys are critical in various manufacturing processes due to their mechanical properties and ability to form durable, machinable alloys. If you’re researching, “Which copper alloys are best for industrial bearings and gears?” consider the following applications.
-
- Machinery and Equipment: Copper alloys like bronze and brass are used in bearings, bushings, and gears due to their strength, wear resistance, and low friction. For example, bronze bearings are common in heavy machinery and marine environments, reducing equipment downtime.
- Heat Exchangers: Copper’s excellent thermal conductivity makes it ideal for heat exchangers in industrial systems, such as those in chemical plants, refineries, and power generation facilities. Copper heat exchangers efficiently transfer heat, contributing to lower energy consumption and improved process reliability.
- Welding and Brazing: Copper is used in welding rods and brazing alloys, providing strong joints in metal fabrication and repair applications.
- Benefits: Copper alloys enhance the durability, efficiency, and safety of industrial equipment, reducing maintenance needs, increasing productivity, and improving performance in high-stress environments.
Search prompt: What are the benefits of using bronze versus brass in heavy machinery applications?
-
- Transportation Sector
Copper plays a vital role in the transportation industry, particularly in automotive, aerospace, railway, and marine applications. If you’re evaluating, “How is copper used in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid cars?” here are key applications:
-
- Automotive Industry: Copper is used in electrical systems (wiring harnesses, motors, batteries), radiators, and brake lines. Electric vehicles (EVs) rely heavily on copper for their motors, batteries, and EV charging station infrastructure due to its unmatched conductivity and reliability.
- Aerospace: Copper alloys are used in aircraft components such as electrical connectors, hydraulic systems, and heat exchangers, where reliability and advanced thermal management are critical for safety and efficiency.
- Marine Applications: Copper-nickel alloys (e.g., CuNi) are used in shipbuilding for piping, heat exchangers, and hull cladding due to their resistance to seawater corrosion and biofouling (marine organism growth).
- Railways: Copper is used in traction motors, overhead power lines, and signal systems, supporting the growing demand for high-speed rail networks.
- Benefits: Copper’s conductivity, corrosion resistance, and durability ensure reliable performance in transportation systems, supporting passenger safety, operational efficiency, and reduced maintenance costs.
Search prompt: How much copper is used in electric vehicles compared to traditional cars? What copper alloys are best for marine environments?
-
- Energy and Renewable Energy
Copper is a cornerstone of both traditional and renewable energy systems due to its conductivity, reliability, and sustainability. If you’re seeking insight into, “Why is copper essential in solar panel manufacturing and wind turbines?” the following details provide an overview.
-
- Power Generation and Transmission: Copper is used in power cables, transformers, and generators to transmit electricity efficiently over long distances with minimal energy loss. Substation equipment and grid infrastructure also depend on copper for optimal performance.
- Renewable Energy Systems: In solar panels, copper is used in photovoltaic cells and wiring to conduct electricity. Wind turbines rely on copper for generators, transformers, and cabling within turbines and between grid connections.
- Energy Storage: Copper is a key component in batteries, particularly lithium-ion batteries used in EVs and grid energy storage, where it serves as a current collector and conductor.
- Benefits: Copper’s high conductivity, durability, and recyclability support efficient energy production and distribution, making it essential for the transition to sustainable and green energy sources.
Search prompt: How does copper contribute to energy efficiency in renewable power systems? What are the best copper products for solar and wind energy projects?
-
- Food and Beverage Industry
Copper’s antimicrobial properties and thermal conductivity make it valuable in food and beverage processing. Wondering, “Is copper cookware safe and what are its benefits in food production?” Consider the following:
-
- Brewing and Distillation: Copper is used in brewing equipment (e.g., stills for whiskey production) because it removes sulfur compounds, improving the taste of the final product. Its thermal conductivity ensures even heating during distillation, supporting quality control in beverage manufacturing.
- Food Processing Equipment: Copper alloys are used in heat exchangers and piping for food processing, where precise temperature control is required for safety and efficiency.
- Antimicrobial Surfaces: Copper’s natural antimicrobial properties (it kills bacteria like E. coli and MRSA) make it suitable for surfaces in food preparation areas, reducing the risk of contamination and supporting food safety compliance.
- Benefits: Copper ensures food safety, enhances production quality, and supports efficient thermal management in food processing environments.
Search prompt: What are the safety standards for copper in food processing equipment? How does copper compare to stainless steel in thermal performance?
-
- Medical and Healthcare Applications
Copper’s antimicrobial properties and biocompatibility make it valuable in healthcare settings. If you’re considering, “How does copper help reduce hospital-acquired infections?” explore these applications:
-
- Medical Equipment: Copper is used in MRI scanners, X-ray machines, and other medical devices due to its conductivity and nonmagnetic nature, which is vital for imaging technologies.
- Antimicrobial Surfaces: Copper and its alloys (e.g., brass) are used for high-touch surfaces like doorknobs, bed rails, and IV poles in hospitals to reduce the spread of infections, supporting infection control protocols.
- Surgical Instruments: Copper alloys are used in some surgical tools due to their durability and resistance to corrosion, ensuring longevity and reliability in critical medical procedures.
- Benefits: Copper helps prevent hospital-acquired infections, supports advanced medical technology, and ensures the reliability of healthcare equipment and infrastructure.
Search prompt: What copper alloys are approved for use in medical devices? How does copper help hospitals meet infection control standards?
-
- Telecommunications
Copper has been a foundational material in telecommunications for decades and continues to play a significant role, even as fiber optic technology advances. If you’re asking, “Is copper still relevant for internet and data transmission?” here’s what to know:
-
- Telephone Lines: Copper wires were historically used for telephone networks and still serve in many areas for landline connections due to their reliability and established infrastructure.
- Internet Infrastructure: Copper cables (e.g., twisted pair wiring) are used in DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) internet connections, providing broadband access in regions without fiber optic infrastructure.
- Benefits: Copper’s conductivity, affordability, and ease of installation make it a reliable choice for telecommunications, especially in areas where fiber optics are not yet available.
Search prompt: What is the future of copper cabling in high-speed networks? How do copper and fiber optic cables compare for business internet solutions?
-
- Consumer Goods and Jewelry
Copper’s aesthetic appeal and workability make it popular in consumer products, art, and jewelry. If you’re searching, “Why choose copper cookware or copper jewelry?” consider the following:
-
- Jewelry and Art: Copper is used in jewelry, sculptures, and decorative items due to its warm color and ability to be shaped into intricate designs. It’s often alloyed with other metals to create unique finishes and visual effects.
- Cookware: Copper pots and pans are prized by chefs for their excellent heat conductivity, ensuring even cooking and precise temperature control in culinary applications.
- Coins: Copper alloys like bronze and brass are used in coinage due to their durability, resistance to wear, and ease of minting.
- Benefits: Copper’s versatility, antimicrobial qualities, and visual appeal make it a favorite for both functional and decorative consumer goods, supporting artisan manufacturing and luxury markets.
Search prompt: What are the advantages of copper cookware over stainless steel? How to care for copper jewelry?
-
- Environmental and Water Treatment
Copper’s properties make it useful in environmental applications, particularly in water treatment and purification systems. If you’re considering, “How does copper improve water quality?” here are some applications:
-
- Water Purification: Copper’s antimicrobial properties help kill bacteria and algae in water systems, making it useful in water treatment plants and swimming pools.
- Desalination Plants: Copper-nickel alloys are used in desalination equipment due to their corrosion resistance in saline environments, supporting global clean water initiatives.
- Benefits: Copper supports clean water initiatives, enhances the durability of water treatment systems, and contributes to environmental sustainability by enabling recyclable and long-lasting infrastructure.
Search prompt: What is the role of copper in modern water purification systems? Which copper alloys are best for seawater applications?
History of Copper
The history of copper dates back to ancient civilizations and is closely tied to the development of human technology. Early copper working processes included coldworking, annealing, smelting, and lost-wax casting. Humans first discovered copper and later its alloy, bronze, around 5500 BC in the Balkans. Approximately 2000 years later, people began alloying copper themselves, marking the start of the Bronze Age. Brass, a copper and zinc alloy, was discovered much later during the Greek period and favored by the Romans for its beauty and corrosion resistance.
Ancient societies across present-day Iran, Turkey, Israel, Egypt, India, Greece, and Rome utilized copper and its alloys for various items like coins, weapons, jewelry, and architecture. The Egyptians were particularly prolific, crafting tools, household items, and even makeup from copper. Despite the discovery of iron and subsequent eras, copper remained significant, with major mining operations like the Falun Mine in Sweden starting around 1000 AD and greatly contributing to European copper supply through the 1600s.
The 1700s saw copper used extensively in European shipbuilding to prevent biofouling of hulls, and by the 1800s, advancements like powder metallurgy and electroplating emerged, enabling new manufacturing techniques. In 1949, the Finnish company Outokumpu revolutionized copper smelting with the energy-efficient flash smelting process, lowering costs and environmental impact. Recognizing copper’s essential role in human health, the EPA set limits on copper levels in drinking water in 1991. Today, copper’s uses continue to expand, especially in telecommunications, electronics, renewable energy, and advanced manufacturing, due to its superconductivity, affordability, and non-sparking nature.
Search prompt: How did the discovery of copper alloys influence ancient civilizations? What are the major milestones in copper metallurgy?
Copper Products
Manufacturers utilize basic copper and copper alloy shape products, such as copper strip and sheet copper, copper foil, copper braid, copper pipes, copper tubes, brass plates, and copper coil, across various industries. These semi-finished copper products serve as the foundation for countless end-use applications.
- Copper strip and sheet are supplied as flat, flexible rolls, ideal for roofing, electrical busbars, and industrial gaskets.
- Copper foil and braid are used in electrical and industrial applications such as electromagnetic shielding, grounding straps, and battery connections.
- Copper tubes and pipes, valued for their corrosion resistance and high heat transfer capabilities, play a crucial role in HVAC, refrigeration, heat exchangers, and plumbing systems.
- Brass plates, available as thin, solid square or rectangular pieces, are used in decorative, architectural, and mechanical applications.
- Copper coils, known for their excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, are used in motors, transformers, inductors, and heating/cooling systems.
Fabricated from these shapes, products include microchips, piping systems, copper cookware, propellers, hardware, tools, lighting fixtures, door handles, fasteners, small springs, roofing materials, coins, electrical connectors, wires, adaptors, and valves, demonstrating their versatility and essential role in modern manufacturing and engineering.
Search prompt: Which copper products are best for HVAC versus plumbing systems? How do you choose between copper sheet and copper coil for your application?
Benefits of Copper
Copper, brass, bronze, and other copper alloys provide numerous advantages for manufacturers, contractors, and end-users. Firstly, copper and its alloys are non-sparking, meaning they do not produce sparks or fires when subjected to friction. This makes them ideal for use in hazardous environments where combustible vapors, gases, and flammable dust are present, such as oil rigs, chemical plants, and grain elevators.
In culinary applications, copper offers superior heat control compared to stainless steel, providing even temperature distribution and responsiveness favored by chefs and food processing professionals.
Beyond their practical benefits, copper and copper alloys are also prized for their aesthetic appeal. Their clean, attractive color and finish make them popular in architectural design, interior décor, and fine art. Various surface treatments can enhance their appearance, giving copper an antique or aged look or protecting it from tarnish.
Another significant advantage of copper is its recyclability. It is one of Earth’s few natural resources that has not been excessively mined. The amount of copper recycled each year nearly matches the amount mined, ensuring its continued abundance. This sustainability, combined with its durability and low maintenance requirements, makes copper a highly favorable material for green building, LEED projects, and circular economy initiatives.
- Corrosion resistance: Ensures longevity even in harsh environments.
- Low maintenance: Reduces long-term costs in infrastructure and manufacturing.
- Biostatic and antimicrobial: Inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi, promoting hygiene and safety.
- Environmentally friendly: Fully recyclable and reusable, contributing to resource conservation.
- High resale value: Scrap copper commands premium prices in the metals market.
Search prompt: What are the environmental benefits of using recycled copper? How does copper compare to aluminum and stainless steel for sustainability?
Choosing the Right Copper Manufacturer or Supplier
If you are in need of copper products for your next project, it is essential to collaborate with a supplier proficient in high-quality copper fabrication and extraction methods. When evaluating copper suppliers, consider factors such as purity, alloy composition, certifications (ISO, RoHS), technical support, delivery times, and value-added services such as custom cutting, forming, and finishing.
- Check for suppliers who offer traceability and material certifications to ensure the copper meets your industry’s regulatory and performance standards.
- Ask about secondary operations such as machining, plating, or assembly, which can streamline your supply chain.
- Consider the supplier’s experience in your target industry (e.g., electrical, HVAC, marine, or food processing) and their track record for on-time delivery.
- Avoid suppliers who offer impure or substandard copper products, as this can compromise safety and performance.
To assist you, we have listed several trusted copper alloy manufacturers and suppliers. Review their profiles to find the right services for your needs. For more options, visit our copper supplier listings.
Search prompt: How do you choose the right copper supplier for specialized applications? What certifications should copper manufacturers provide?
Whether you’re planning a large-scale construction project, fabricating precision electronics, or sourcing materials for renewable energy systems, copper remains one of the most reliable, sustainable, and high-performance metals available. Explore your options, compare products, and partner with a reputable supplier to maximize the benefits of copper in your next application.
Why is copper commonly used in electrical wiring and electronic devices?
Copper is widely used in electrical wiring and electronic devices because it has excellent electrical conductivity, ductility, and corrosion resistance. These properties ensure efficient power transmission, minimal energy loss, and reliable long-term performance in a variety of electronic systems.
What are some common applications of copper alloys like bronze and brass?
Copper alloys such as bronze and brass are used in bearings, gears, coins, decorative elements, machinery, marine components, and musical instruments. Alloying copper with tin or zinc improves mechanical and chemical properties, broadening the range of industrial, architectural, and artistic applications.
How does copper benefit the construction and architecture industry?
Copper’s durability, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic appeal make it ideal for roofing, cladding, plumbing, wiring, and decorative features in buildings. It develops a protective patina over time, offering long service life with minimal maintenance in both residential and commercial structures.
What makes copper important in renewable energy systems?
Copper is essential in renewable energy systems because of its high electrical and thermal conductivity, which improve efficiency in solar panels, wind turbine generators, and energy storage batteries. Its reliability and recyclability also support sustainable green energy infrastructures.
How do the antimicrobial properties of copper enhance safety in healthcare and food industries?
Copper’s natural antimicrobial properties help kill bacteria and fungi, making surfaces and equipment safer in healthcare and food processing. Applications include high-touch surfaces in hospitals and heat exchangers or piping in food production, where copper reduces contamination risks and promotes hygiene.
What are the environmental benefits of using copper and its alloys?
Copper is fully recyclable, with nearly as much copper recycled each year as is mined. Its long life, recyclability, and ability to be reused in new applications contribute to resource conservation and support green building, sustainability, and circular economy initiatives worldwide.
What factors should be considered when choosing a copper supplier or manufacturer?
When selecting a copper supplier, consider factors such as purity, alloy composition, certifications (like ISO or RoHS), technical support, traceability, delivery times, and offered value-added services including custom cutting or finishing to ensure the copper meets your project’s standards and requirements.






 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers Aluminum
Aluminum Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze Magnets
Magnets Nickel
Nickel Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers Titanium
Titanium Tungsten
Tungsten Wire Rope
Wire Rope Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services